|
CS6320: SW Engineering of Web Based Systems |
||||||
|
NodeJS
What is NodeJS and what is MEAN
NodeJS = asynchronous event driven JavaScript runtime, Node is designed to build scalable network applications. In the following "hello world" example, many connections can be handled concurrently. Upon each connection the callback is fired, but if there is no work to be done Node is sleeping *******It has a built in HTTP server library --- you don't need a separate web server like Apache --- the nodeJS application can do the http listening -----*********************** simple NodeJS application that is an http listener and always returns Hello World This is in contrast to today's more common concurrency model where OS threads are employed. |
|
WHY NodeJS?
-
Asynchronous i/o framework
-
can be faster as event driven
-
can process more requests / second that competitors like RoR and Java
-
-
Single Thread with Event Loop-->speed
-
many many modules
1 Language for Frontend and Backend
-
There are a number of NodeJS frameworks that extend its capabilities and help with MVC
(i.e. Express, Meteor)
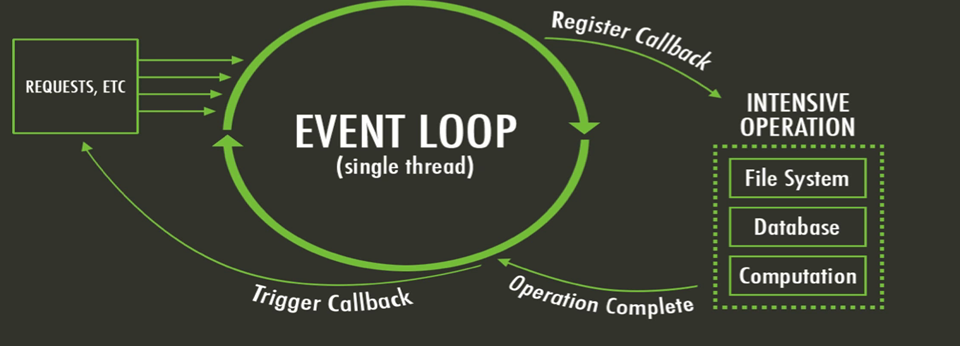
There are a couple of implications of this apparently very simple and basic model
•Avoid synchronous code at all costs because it blocks the event loop•Which means --> create callbacks!!!!!!!
When do you use NodeJS
● Web application
● web socket app
● Ad server
● Proxy server
● Streaming server
● Fast file upload client
● Any Real-time data apps
● Anything with high I/O
● chat/messaging
● realtime applications
● high concurrency applications
● communication hubs
● recommendation systems
● MORE MORE MORE
First -- Learn basic syntax of Javascript - see CS3520
|
 |
NodeJS basics
we will learn as we go..do recommended reading
NodeJS modules
- Many NodeJS programs leverage the use of module (think of this like libraries or packages in other languages)
- A module encapsulates related code into a single unit of code. (like packages in Java)
- You can use other peoples modules or create your own
2 Ways to create a module
module.exports = { sayHelloInEnglish: function() { return "HELLO"; }, sayHelloInSpanish: function() { return "Hola"; } };// greetings.js var exports = module.exports = {}; exports.sayHelloInEnglish = function() { return "HELLO"; }; exports.sayHelloInSpanish = function() { return "Hola"; };
how to import (require) a module into a NodeJS file
The keyword
// main.js var greetings = require("./greetings.js"); // "Hello" greetings.sayHelloInEnglish(); // "Hola" greetings.sayHelloInSpanish();requirereturns an object, which references the value ofmodule.exportsfor a given file
how to install a module in your application director
$npm install <module name>
Installation, Application Setup and using Heroku
- install NodeJS and npm
- The application directory structure and running on command line
- Creating a BASIC NodeJS application (using Express framework for routing) and running locally
- More about Express
- Using Heroku for hosting and its deployment tools
using NodeJS to connect and use a MongoDB database