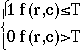|
Binary Images
A Binary Image is one whose pixels take on a value of 0 or 1 (or some
other 2 valued set of numbers....like 0 and 255).
Why Binary Images?
- Analysis: Use to separate objects from the background. E.g. OCR, Object
Recognition by Silhouette Tracing.
- Art.
- Reduced Storage and faster calculations
How to Create a Binary Image
Binary Image = Thresholded Original Image |
Thresholding an Image
binary(r,c) = binary image pixel (r,c)
f(r,c) = original image pixel (r,c)
T = threshold value
at every pixel location (r,c)
in the image set:
binary(r,c) = 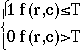 |
Example
Save have a greyscale image with 256 greylevels
i.e. p(r,c) = {0, 1, 2, .... 255}
say T = 100
then if p(r,c) <= 100 -----> binary(r,c)=1
else if p(r,c) > 100 -----> binary(r,c)=0 |
How to pick T?
Want T such that only pixels belonging to object you want to highlight are
greater than T.
- Trial and Error
- Can use the Image's Histogram to Pick T.
|
Pick T Threshold using Histogram
- Look at a plot of h(m) and look for a valley to separate the objects pixels
from the rest of the image. For example, suppose h(m) takes on the following
bi-modal shape.
What about a Color Image?
Color image: f(r,c) = (red,green,blue)
e.g. f(r,c) = (255,255,255)= white color
f(r,c) = (0, 0, 0) = black color
1) Create a histogram for each color and create three binary images one for
each color field: h red(), h green(), h blue()
2) Convert color to greyscale first as shown below and then threshold the new
greyscale image:
greyscale value = f'(r,c) = (red + green + blue)/
Example: Find the coin
 |
 |
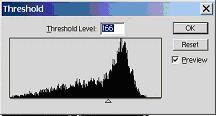
Histogram and selected threshold level, Pick Threshold right where it seperates lighter backbround from darker coin pixels.
|
|
|