|
||||||
|
The Lens
The Pinhole camera
- Ideally have infinite depth of focus and no distortion.
- Projects light on to image plane from the pinhole lens
- Problem- light gathering ability is poor and exposure time needed is long.
Solution- The LENS
Optical axis- Connects center of image plane through the center of lens
(focal point).
Focal length- Distance of the image plane from the optical origin (center of lens) when parallel rays are focused onto a single point in the image plane.
|
The Lens Law:
|
Lens Properties..................
Depth of Field = is determined by the distance from the nearest object
plane in focus to that of the farthest plane also simultaneously in focus.
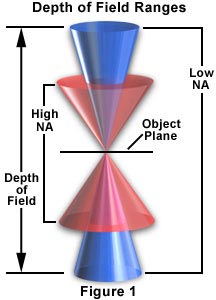
The Equation: r= Depth of field = 2cn(m+1)/(m*m)
- n = f-stop

n = f/d - f = fixed focal length
- d = diameter of aperture
- c = constant
- m = v/u
- As d decreases, r increases
Perspective Projection
How 3D points project into their 2D coordinates on the image plane.
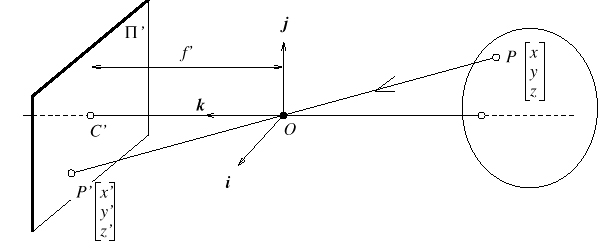
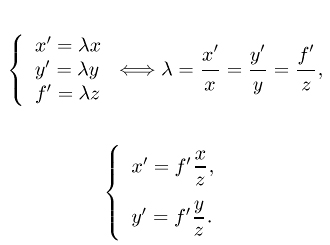
- Line of sight- line connecting object point in 3D through the focal
point.
- Corresponding Image Point- Where the line of sight hits the image
plane.
- The further away the object is, the smaller it will be projected onto
the image plane.
- The closer the object is, the larger the projection into the image plane.
- A point in the world (3D) projects into a single point on the image.
- A point in the image can be the result of any world point (3D).
