|
Main Menu
|
Section Menu
|
Syllabus
|
Previous
|
|
|
Next |
| Architecture | Page 1 of 7 |
VoiceXml is the driving force for voice portals and voice applications.
The main components and functions of the architecture are classified as follows:
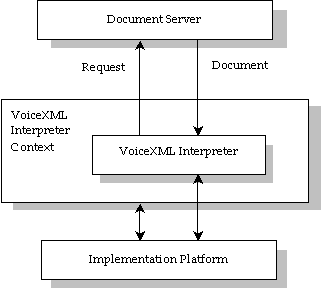
Figure 2.1: Architectural Model (from W3C.org)
Document Server:
The document server runs the application logic. It contains the database or acts as an interface to an external database or transaction server. It process request from the client application the VoiceXML interpreter by replying with VoiceXML document which contain the actual VoiceXML commands.
VoiceXML Interpreter:
The VoiceXML interpreter processes the commands from the VoiceXML document through the VoiceXML interpreter. It plays the prompts, listens to responses and executes the logic to guide a caller through the application according to the VoiceXML document obtained from the server. It also retrieves content from the websites to play back to the caller. All the events are executed according to the VoiceXML document.
VoiceXML Interpreter Context:
The VoiceXML interpreter context is responsible to detect any incoming calls, acquire the VoiceXML document and answer the calls. It also monitors the caller input and control the implementation platform along with the VoiceXML interpreter.
Implementation Platform:
The implementation platform contains the telephone hardware and related resources. It generates events in response to the caller actions (for example spoken or cahracter input received, disconnect) and system events (example timer expiration)
|
Main Menu
|
Section Menu
|
Syllabus
|
Previous
|
|
|
Next |