|
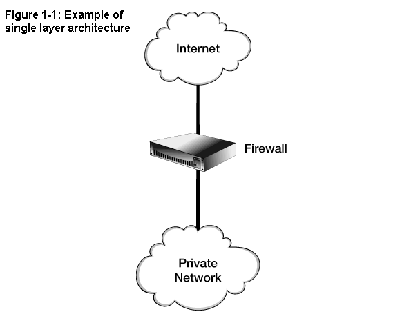
Single Layer
- one network host is allocated all firewall functions
- onnected to each network for which it is to control access.
- chosen when containing cost is a primary factor or when there
are only two networks to interconnect.
- +: everything there is to know about the firewall resides
on that one host.
- ok: In cases where the policy to be implemented is simple
and there are few networks being interconnected,
- +: cost-effective to operate and maintain over time.
- -: susceptibility to implementation flaws or configuration errors
— depending on the type, a single flaw or error might allow firewall
penetration.
|
 |
|
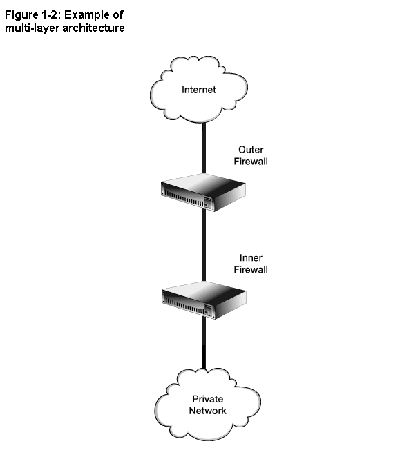
Multi- Tier
- firewall functions are distributed among a small number of
hosts, typically connected in series.
- -: more difficult to design and operate
- +:can provide substantially greater security by diversifying
the defenses you are implementing.
- -: more costly
- note: possibly using different technology in each of
these firewall hosts. This reduces the risk that the same implementation
flaws or configuration errors will exist in every layer.
|
 |
|

