Here you will find information on:
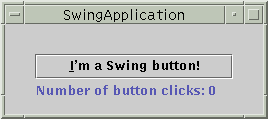
Swingimport javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class SwingApplication {
private static String labelPrefix = "Number
of button clicks: ";
private int numClicks = 0;
public Component createComponents() {
final JLabel label =
new JLabel(labelPrefix + "0 ");
JButton button = new
JButton("I'm a Swing button!");
button.addActionListener(new
ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
numClicks++;
label.setText(labelPrefix + numClicks);
}
});
/*
* An easy way
to put space between a top-level container
* and its contents
is to put the contents in a JPanel
* that has an
"empty" border.
*/
JPanel pane = new JPanel();
pane.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(
30, //top
30, //left
10, //bottom
30) //right
);
pane.setLayout(new GridLayout(0,
1));
pane.add(button);
pane.add(label);
return pane;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(
UIManager.getCrossPlatformLookAndFeelClassName());
} catch (Exception e)
{ }
//Create the top-level
container and add contents to it.
JFrame frame = new JFrame("SwingApplication");
SwingApplication app
= new SwingApplication();
Component contents =
app.createComponents();
frame.getContentPane().add(contents,
BorderLayout.CENTER);
//Finish setting up the
frame, and show it.
frame.addWindowListener(new
WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}

Java automatically reclaims memory used by an object when no object variables refer to that object.
b1 = new Button("Test Button");
b1 = new Button("Another Button");
Nothing points to first object("Test button"). It will be garbage collected.
b1 = new Button("Test Button");
b2 = b1;
b2 = new Button("Another Button");
First object is not garbage collected because b1 still refers to it.
You can call System.gc() to manually invoke garbage collection.
javac
java compiler. Converts java source code into bytecodes.
javac -verbose calculator.java
Tells you which other java classes the compiler needs to create the compile class file and how long it took to do the compilation.
java
java interpreter.
java -prof helloworld.java
Analyzes how much time the program spends in each part of the code. It creates a file called java.prof This file shows how many times each method was called and how many miliseconds were spent executing each one.
javadoc
Automatically generates HTML documentation for your code.
/** testdoc - A test file for documentation of JDK */
public class testdoc {
/** This methiod is called first by the
java interpreter.
It prints a message
to the console */
// javadoc will ignode this commnet
public static void main(String[] argv)
{
/* javadoc will also
ignore this comment */
System.out.println("JDK
Test");
}
}
javadoc testdoc.java
Will create a testdoc.html file that uses the comments beginning with multiple asterisks.
javah
Given a class file, generates the C header files needed by C programs to access the class's data. Performance critical parts of the code can be written in C for better speed.
javah Filecopy
will create the file Filecopy.h Note that Filecopy is the name of the class not the file.
jdb
Java debugger. Use to monitor and control execution of a java program so that bugs can be found.
alpha>jdb testdoc
Initializing jdb...
0xad:class(testdoc)
> stop in testdoc.main
Breakpoint set in testdoc.main
> run
run testdoc
Breakpoint hit: running ...
testdoc.main (testdoc:12)
main[1] main[1] list
8
// javadoc will ignode this commnet
9
10
public static void main(String[] argv) {
11
/* javadoc will also ignore this comment */
12 =>
System.out.println("JDK Test");
13
}
14
}
main[1] clear testdoc.main
Breakpoint cleared at testdoc.main
main[1] cont
main[1] JDK Test
testdoc exited
Type help at jdb prompt to get a list of options.
javap
Examines the bytecodes of a compiled class file and identify its accessible variables and functions.
javap testdoc
Compiled from testdoc.java
public class testdoc extends java.lang.Object
{
public testdoc();
public static void main(java.lang.String[]);
}
javap -c testdoc
shows each step that will be taken by the VM to execute the class.
Send comments to msun@cis.ohio-state.edu