|
CS6320: SW Engineering of Web Based Systems |
||||||
|
PHP to perform authentication
NOTE: The signed_request parameter is utilized to share information between Facebook and app in a number of different scenarios:
- A signed_request is passed to Apps on Facebook.com when they are loaded into the Facebook environment
- A signed_request is passed to any app that has registered an Deauthorized Callback in the Developer App whenever a given user removes the app using the App Dashboard
- A signed_request is passed to apps that use the Registration Plugin whenever a user successfully registers with their app
The signed_request parameter is the concatenation of a HMAC SHA-256 signature string, a period (.), and a base64url encoded JSON object. It looks something like this (without the newlines):
vlXgu64BQGFSQrY0ZcJBZASMvYvTHu9GQ0YM9rjPSso . eyJhbGdvcml0aG0iOiJITUFDLVNIQTI1NiIsIjAiOiJwYXlsb2FkIn0
NOTE: Because of the way that we currently load iframes for Apps on Facebook.com, it is important that you navigate the top window of the user's browser to the OAuth Dialog. Many apps do this by sending a script fragment to the user's browser setting the top.location.href property to the dialog URL. Please see the PHP example at the end of this section for an example.
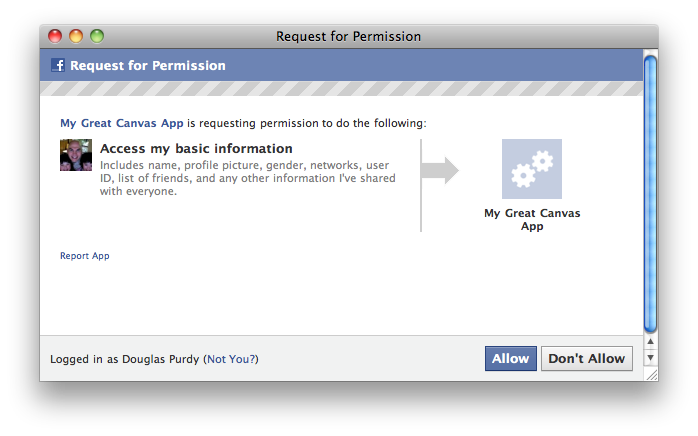
Here is some code to do "authentication" via access of the signed_request parameter and prompt the user to authorize your app:
<?php
$app_id = "YOUR_APP_ID";
$canvas_page = "YOUR_CANVAS_PAGE_URL";
$auth_url = "http://www.facebook.com/dialog/oauth?client_id=". $app_id . "&redirect_uri=" . urlencode($canvas_page);
$signed_request = $_REQUEST["signed_request"]; // this will be passed automatically (see above) to
// your app when user invokes
list($encoded_sig, $payload) = explode('.', $signed_request, 2);
$data = json_decode(base64_decode(strtr($payload, '-_', '+/')), true);
if (empty($data["user_id"])) { // if no data given about user in signed_request info then ask user
// to authorize your app to get it
// facebook will return to the canvas_page as a "call back " url
//and pass the new signed_request
echo("<script> top.location.href='" . $auth_url . "'</script>");
} else {
echo ("Welcome User: " . $data["user_id"]);
}
?>