High Volume Design
- limitations of bandwidth
- single versus multiple servers.
|
A Theoretical Performance Metric
- Lack of Performance = requests * (Database Weight + Content
Complexity)
- Requests = This is the number of hits, or requests for
content.
- Database Weight = This is a reflection of table sizes, query
complexity, and general efficiency of database requests.
- Content Complexity = measure of dynamic content. A site
is complex if you use a lot of cgi applications, or applications
that are resource intense, and if there is extensive use of
visual content and page elements on the site.
|
Evolution of a Site
Small Site
- one server
- serves as web-page, application and database servers,
every thing
- fine with "lite" traffic
|
Buy more Powerful Server
- Typically will increase speed and throughput but.............
- Buying a more powerful server can often fail to provide
the desired result, since software isn't always predictable
in the way it scales due to complex hardware/sofware issues.
Will your software take advantage of multiple processors
when available?
- Database access can be improved by changing platform.
Some software like ZCache
which is lower cost and can help.
|
Seperate Content from Application Server and/or Data Server
- first step in "growth" is to move applicatons
to their own server
- similarly may move database to seperate server
- advantages in security also.
- move off resources to a seperate server by the load/use
the have.
|
Load Balancing with Multiple Servers....add more
- no one technique to the design here.
- some application-specific designs/techniques like "Distributed
Databases".
- hardware versus software techniques:
- The two most common kinds of balancers are 'Round-Robin'
and 'Intelligent'. These terms are related
to the algorithms used to balance the load.
- A Round-Robin hardware load balancer
alternately routes a request to the next server in it's
list in a specific order.
- These routers help, but suffer from 'hotspots'
created by a number of requests stacking up on one
server from time to time. This occurs because the
router has no way to determine the weight (or resource
requirement) of any specific request.
- When using this technique all servers in the cluster
are loaded to serve the same content so they can
handle any request.
- An intelligent load balancer (software
based) attempts to determine which server is least loaded,
and route the request to the server most likely to be
able to handle the request quickly.
- High quality software load balancers are more
expensive than round robin.
- An intelligent load balancing scheme features
different numbers of servers in groups or clusters
dedicated to performing specific operations (ie.
search engines, static content, servlet servers,
etc.).
- This means that computing power can be allocated
based on the requirements of the content provider
and resources needed to supply specific content.
- Example: ZAppSvr
is an intelligent load balancer
|
|
Logical Layer of Architecture : N-Tier Architecture
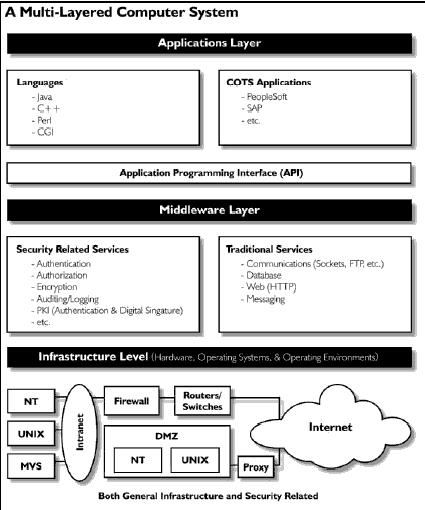
|
Architecture Design Techniques
- is new, no standard methodology for developing enterprise architecture.
Basically, can approach many different ways. Data-driven, User-driven,
Function-driven. Can develop each sub-system using appropriate
techniques. Can try using techniques similar to "software
engineering" techniques to design at the entire/enterprise
system level.
- Example:
Open Group Architectural Framework (TOGAF) Method for
developing Enterprise Architectures.
- It is a tool that enables you to design, evaluate, and
build the right architecture for your organisation.
- It is published by The Open Group on its public web site,
and can be used free of charge by any organisation wishing
to develop an information systems architecture for internal
use.
- TOGAF can be used for developing a broad range of different
IT architectures.
- It describes a method for designing an information system
in terms of a set of building blocks, and incorporates a set
of tools, a common vocabulary, and a list of recommended standards
and compliant products.
|
Re-Design Issues
- Profiling is the process of collecting information about
your users. Can custom make software. Also, some systems, shrink-wrapped
solutions. Example: Microsoft
Commerce Server.
|
Web Application Servers
- many
- platform specific, language specific
|
|