- AJAX is not a new programming language, but simply a new technique
for creating better, faster, and more interactive web applications.
- AJAX uses JavaScript to send and receive data between a web
browser and a web server.
- makes web pages more responsive by exchanging data with the
web server behind the scenes, instead of reloading an entire web
page each time a user makes a change.
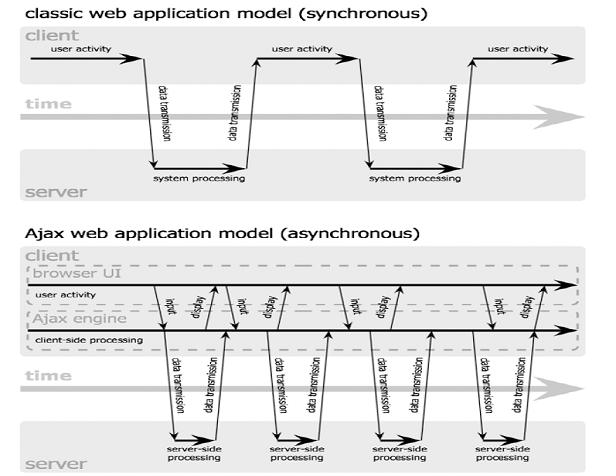
- AJAX is a technology that runs in your browser as it uses JavaScript
- It uses asynchronous data transfer (HTTP requests) between the
browser and the web server, allowing web pages to request small
bits of information from the server instead of whole pages. The
technology makes Internet applications smaller, faster and more
user friendly. lamp AJAX is a web browser technology independent
of web server software.
- Why AJAX? More stuff is
done on the client side. In some instances an Ajax based site
will load quicker than a comparable traditional Web site. Uses callback function that manipulates the page using DOM.
- Note: Asynchronous meansthe ability to handle processes independently
from other processes
- Uses:
|
Advantages and Disadvantages?
Whats really NEW HERE? These techniques have been available
to developers targeting Internet Explorer on the Windows platform
for many years. Until recently, the technology was known as web
remoting or remote scripting. Web developers have also used a combination
of plug-ins, Java applets, and hidden frames to emulate this interaction
model for some time. What has changed is that the inclusion of
support for the XMLHttpRequest object has became ubiquitous
in the mainstream browsers across all platforms. The real magic
is the result of the JavaScript technology's XMLHttpRequest object.
Although this object is not specified in the formal JavaScript technology
specification, all of today's mainstream browsers support it. The
subtle differences with the JavaScript technology and CSS support
among current generation browsers such as Firefox, Internet Explorer,
and Safari are manageable. If you are required to support older
browsers, AJAX may not be the answer for you.
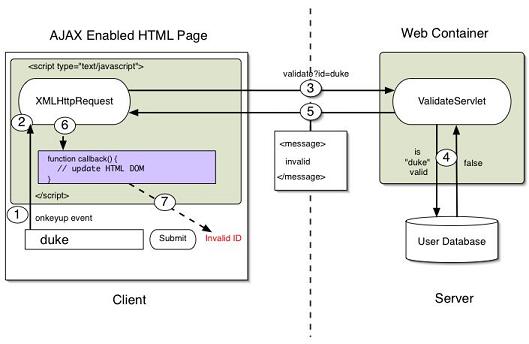
Example: AJAX calling a Java Servelet as the server program.
- Applications Include:
- Real-Time Form Data Validation: Form data
such as user IDs, serial numbers, postal codes, or even special
coupon codes that require server-side validation can be validated
in a form before the user submits a form.
- Autocompletion: A specific portion of form
data such as an email address, name, or city name may be autocompleted
as the user types.
- Master Details Operations: Based on a client
event, an HTML page can fetch more detailed information on
data such as a product listing that enables the client to
view the individual product information without refreshing
the page.
- Sophisticated User Interface Controls: Controls
such as tree controls, menus, and progress bars may be provided
that do not require page refreshes.
- Refreshing Data on the Page: HTML pages may
poll data from a server for up-to-date data such as scores,
stock quotes, weather, or application-specific data.
-
Server-side Notifications: An HTML page may
simulate a server-side push by polling the server for event
notifications that may notify the client with a message,
refresh page data, or redirect the client to another page.
- Possible Problems (exist for other technologies too!)
- Complexity: Server-side developers
will need to understand that presentation logic will be required
in the HTML client pages as well as in the server-side logic
to generate the XML content needed by the client HTML pages.
HTML page developers must have JavaScript technology skills.
Creating AJAX-enabled applications will become easier as new
frameworks are created and existing frameworks evolve to support
the interaction model.
- Standardization of the XMLHttpRequest Object:
The XMLHttpRequest object is a newer part of the JavaScript
technology specification, which means that the behavior
may vary depending on the client and its uspport of JavaScript.
-
JavaScript Technology Implementations: AJAX
interactions depend heavily on JavaScript technology, which
has subtle differences depending on the client. See QuirksMode.org
for more details on browser-specific differences.
-
Debugging: AJAX applications are also difficult
to debug because the processing logic is embedded both in
the client and on the server.
-
Security & Viewable Source: The client-side
JavaScript technology may be viewed simply by selecting
View Source from an AJAX-enabled HTML page. A poorly designed
AJAX-based application could open itself up to hackers or
plagiarism.
|

