|
Remove DC component
The algorithm removes any DC offset in the signal. This is a
very important step because the zero-crossing rate of the signal
is calculated and plays a role in determining where unvoiced sections
of speech exist. If the DC offset is not removed, we will be unable
to find the zero-crossing rate of noise in order to eliminate
it from our signal.
|
|
Threshold determination: via computing average magnatude and
zero-crossing rates.
Compute the average magnitude and zero-crossing rate of the signal
as well as the average magnitude and zero-crossing rate of background
noise.
The average magnitude and zero-crossing rate of the noise
is taken from the first hundred milliseconds of the signal.
The means and standard deviations of both the average magnitude
and zero-crossing rate of noise are calculated, enabling
us to determine thresholds for each to separate the actual speech
signal from the background noise.
|
|
Signal speration from noise. Done using tresholds from previous
step.
At the beginning of the signal, we search for the first point
where the signal magnitude exceeds the previously set threshold
for the average magnitude. This location marks the beginning of
the voiced section of the speech.
starting point of speech = first
point a sample's magnitude > noise magnatude thershold.
|
Detection of "unvoiced" sound starting speech utterance
(may not exist)
- From this point, search backwards until the magnitude drops
below a lower magnitude threshold.
- From here, we search the previous twenty-five frames of the
signal to locate if and when a point exists where the zero-crossing
rate drops below the previously set threshold. This point, if
it is found, demonstrates that the speech begins with an unvoiced
sound and allows the algorithm to return a starting point for
the speech, which includes any unvoiced section at the start of
the phrase.
|
|
Repeat above steps for the end of the speech signal.
|
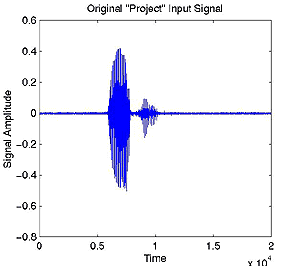
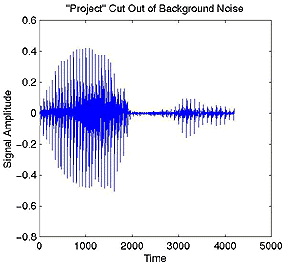 Output
Signal containing only Speech
Output
Signal containing only Speech