Example
Consider the following
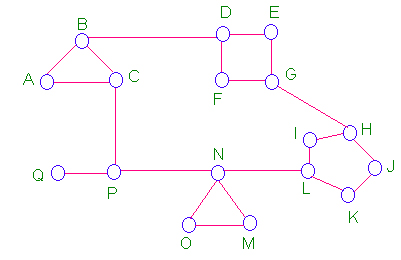
network graph. If we use a DV algorithm, each node of the network
has to have a routing table with 17 entries
Original Network and DV
routing Table for node A.
| Destination |
Line |
Weight |
| A |
----- |
----- |
| B |
B |
1 |
| C |
C |
1 |
| D |
B |
2 |
| E |
B |
3 |
| F |
B |
3 |
| G |
B |
4 |
| H |
B |
5 |
| I |
C |
5 |
| J |
C |
6 |
| K |
C |
5 |
| L |
C |
4 |
| M |
C |
4 |
| N |
C |
3 |
| O |
C |
4 |
| P |
C |
2 |
| Q |
C |
3 |
1) Group Network into Regions, here we
do 5.
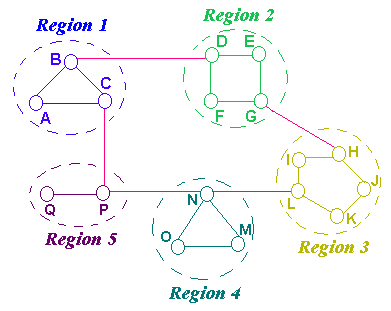
2)From Routing Table for each node in each Region. Example for
node A. We only record info about other routers in the same region
and also the best single hop to the
"bridge" to other regions in the network.
| Destination |
Line |
Weight |
| A |
---- |
---- |
| B |
B |
1 |
| C |
C |
1 |
| Region 2 |
B |
2 |
| Region 3 |
C |
2 |
| Region 4 |
C |
3 |
| Region 5 |
C |
4 |
Multi-level Hierarchical Routing
This example shows
a 2 level hierarchical routing. We can also use 3 or 4 level
hierarchical routing. In 3 level hierarchical routing, network
classified to number of “Clusters”. Each cluster
is made up number of regions (and each region contains a number of
routers).
|
Internet Routing
Hierarchical routing
(variations of) is widely used along with other routing
protocols.
|
|

