ADT: Abstract Data Type
The description of a data type is distinct from its computer implementation
An abstract data type defines a data type in
terms of a type and a set of operations on the type
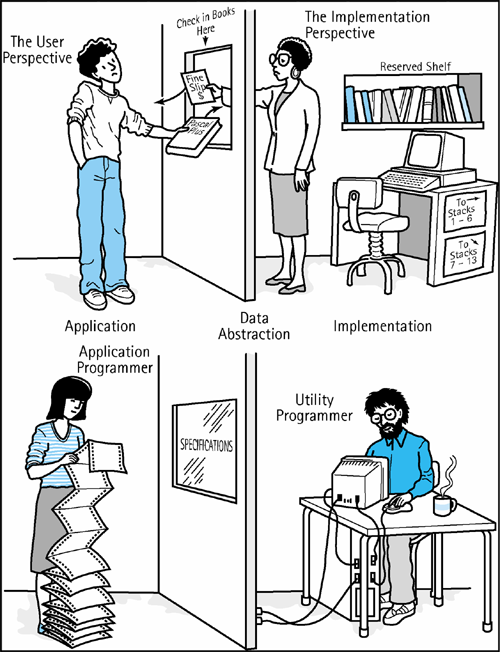
Data at 3 different Levels
Application (or user) level: modeling real-life data in a specific context.
Logical (or ADT) level: abstract view of the domain and operations. ...WHAT
Implementation level: specific representation of the structure to hold the data items, and the coding for operations. .......HOW
|
|
Abstract Data Type
|
Data Structure
|
Understanding ADTs is understanding how to manage complexity through
abstraction
|
Example: A library
|
ADT Operator Categories |
|
Constructors
|
|
Transformers/ Mutators
|
|
Observers
|
|
Iterators
|